During the Indian Wars of the 1860s and 1870s, all sides fought to control the land, travel safely, and protect their families and their futures.
Indian Wars
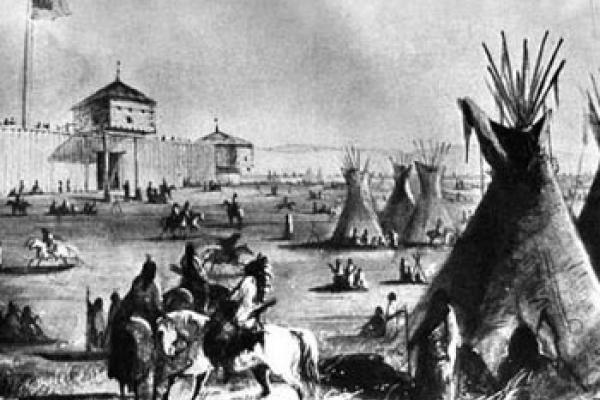
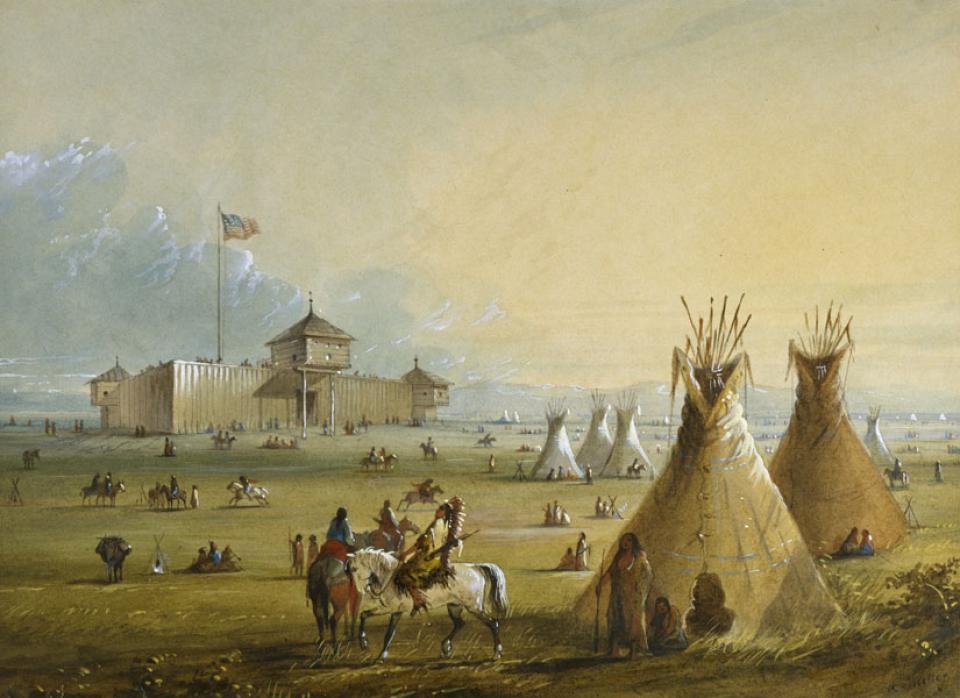
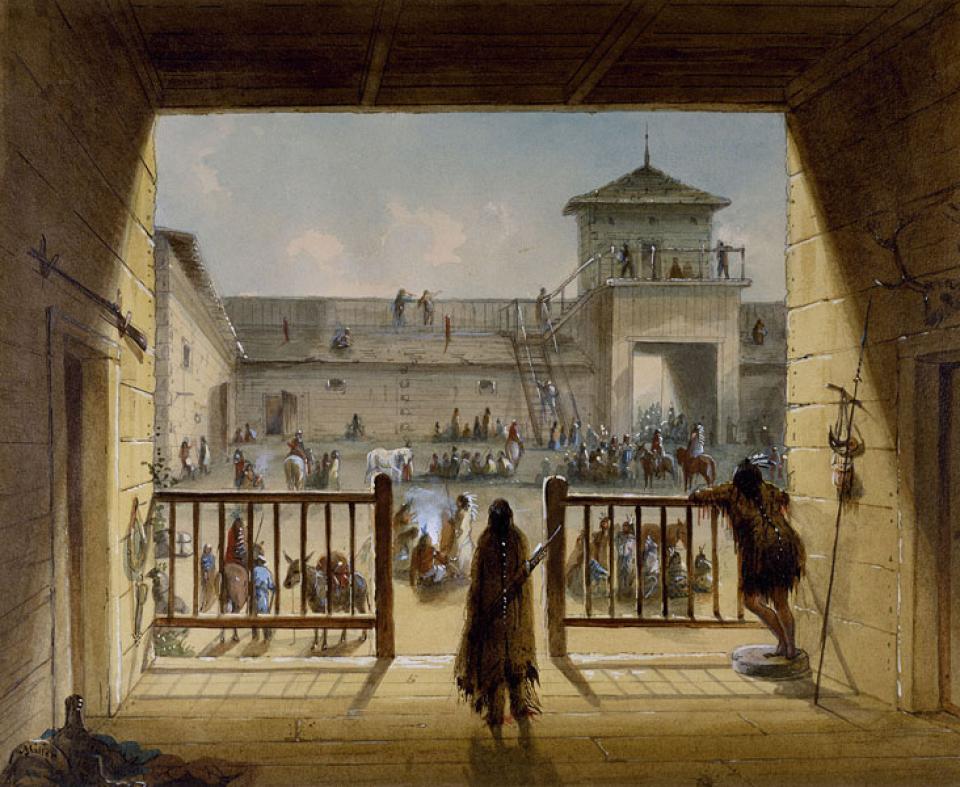
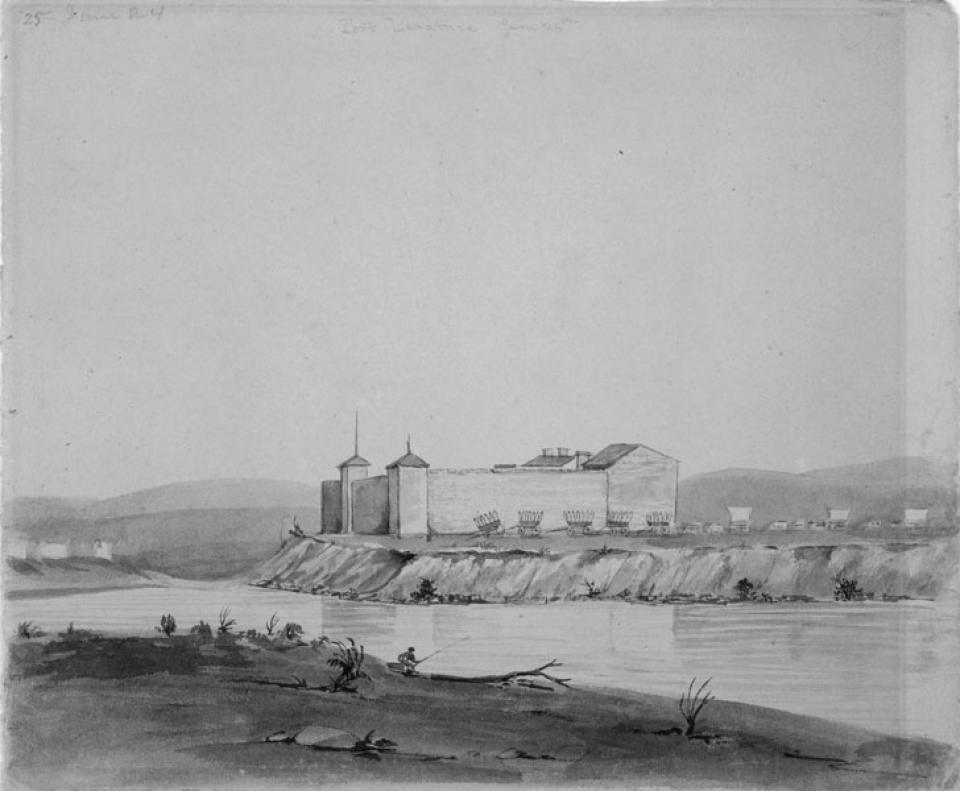
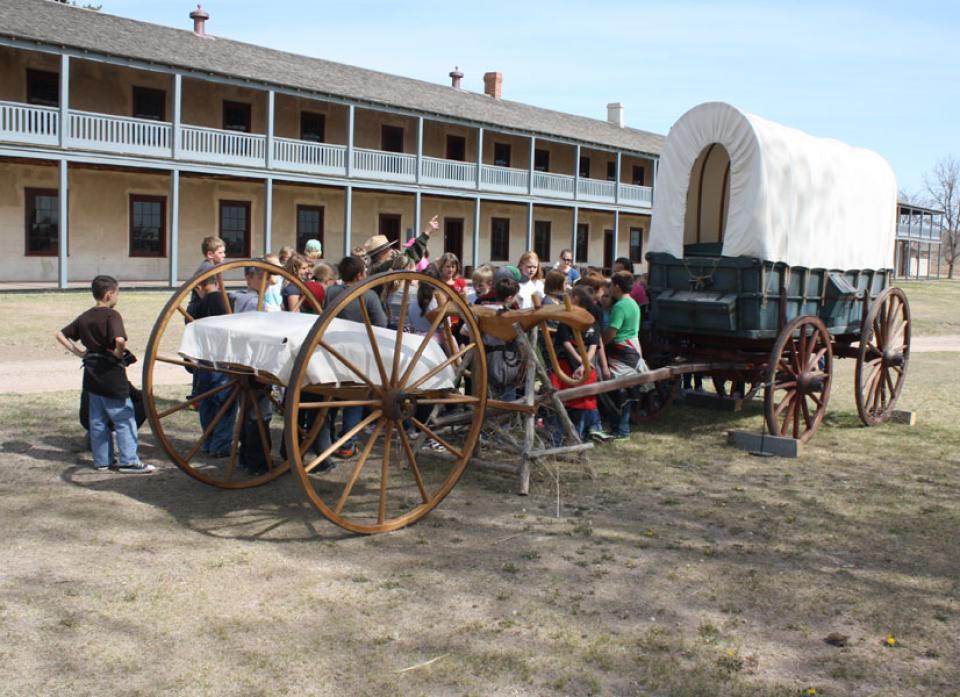
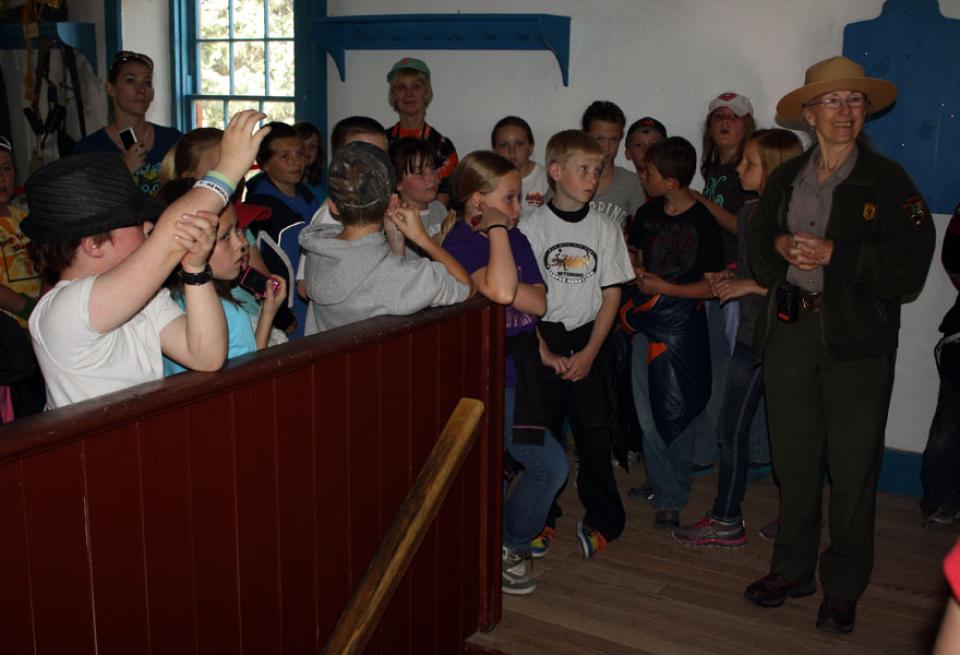
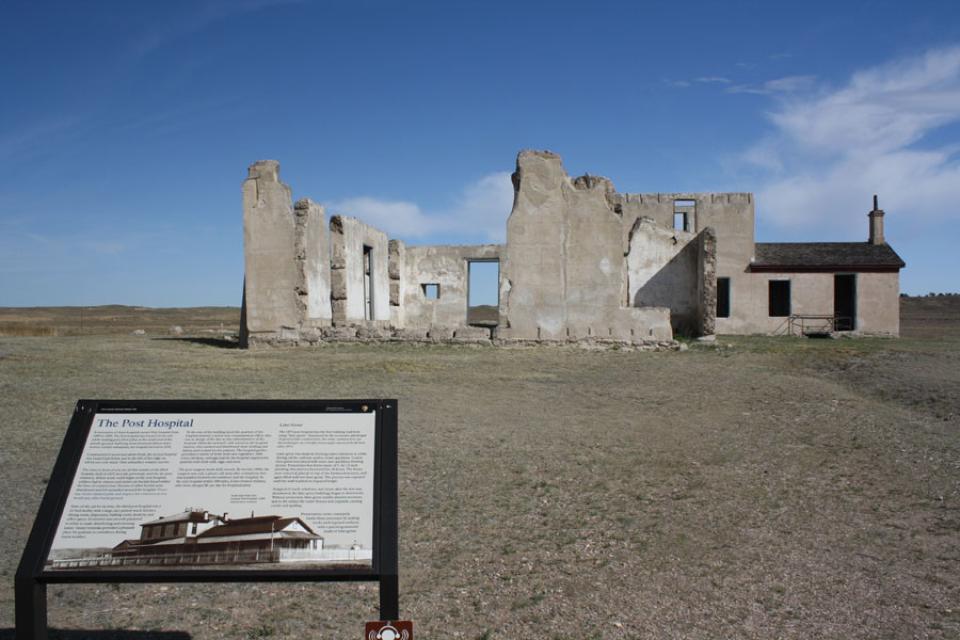
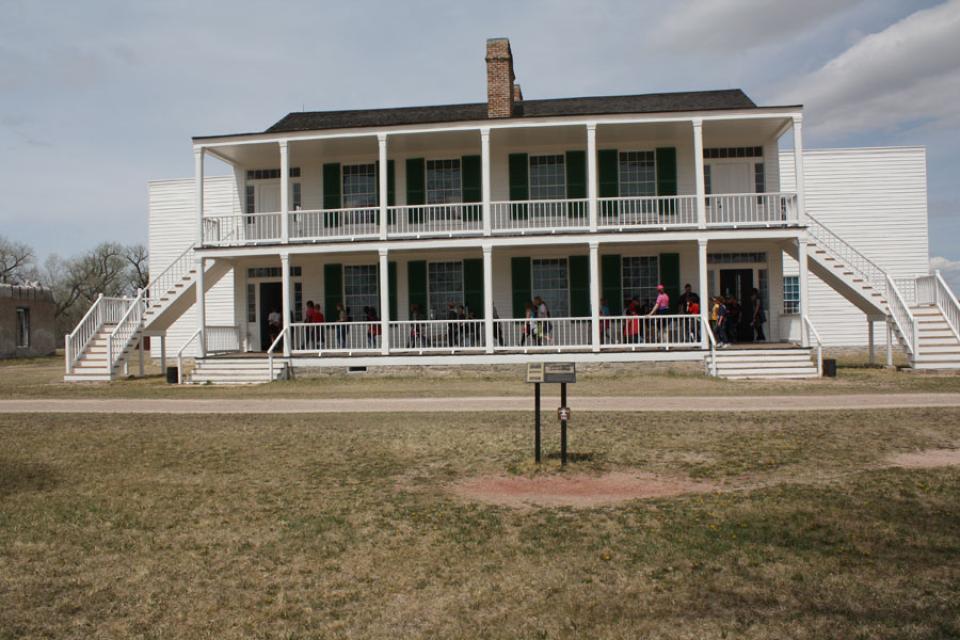
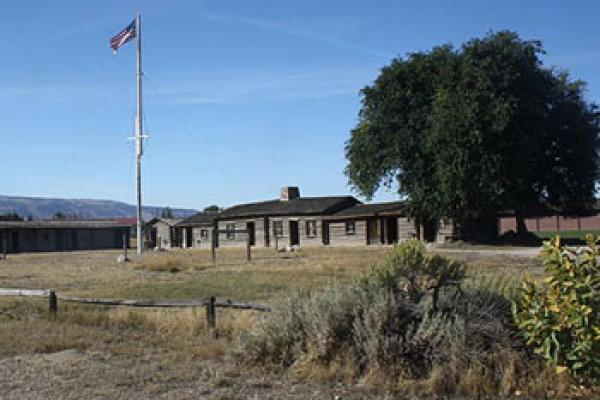
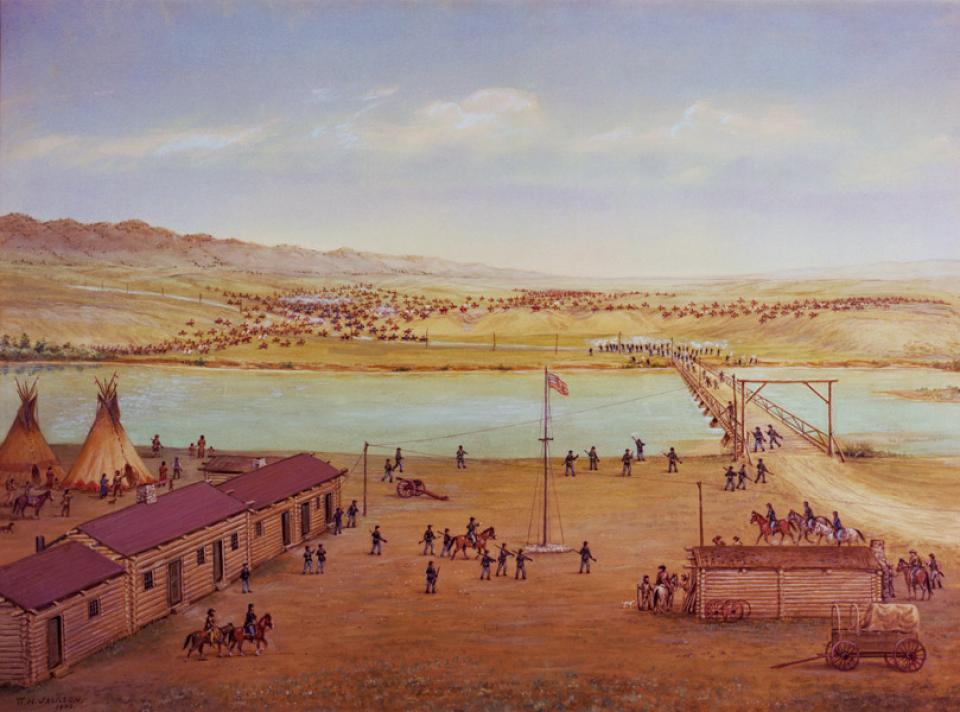
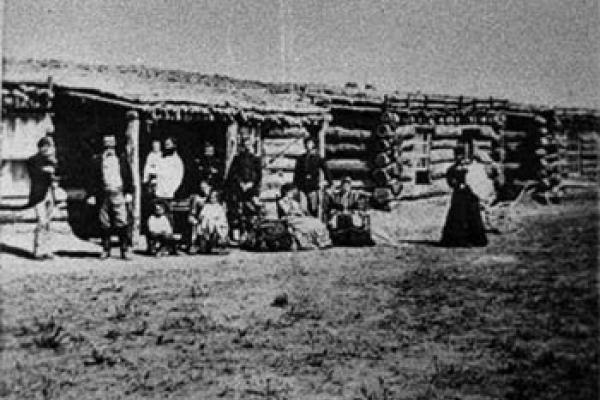
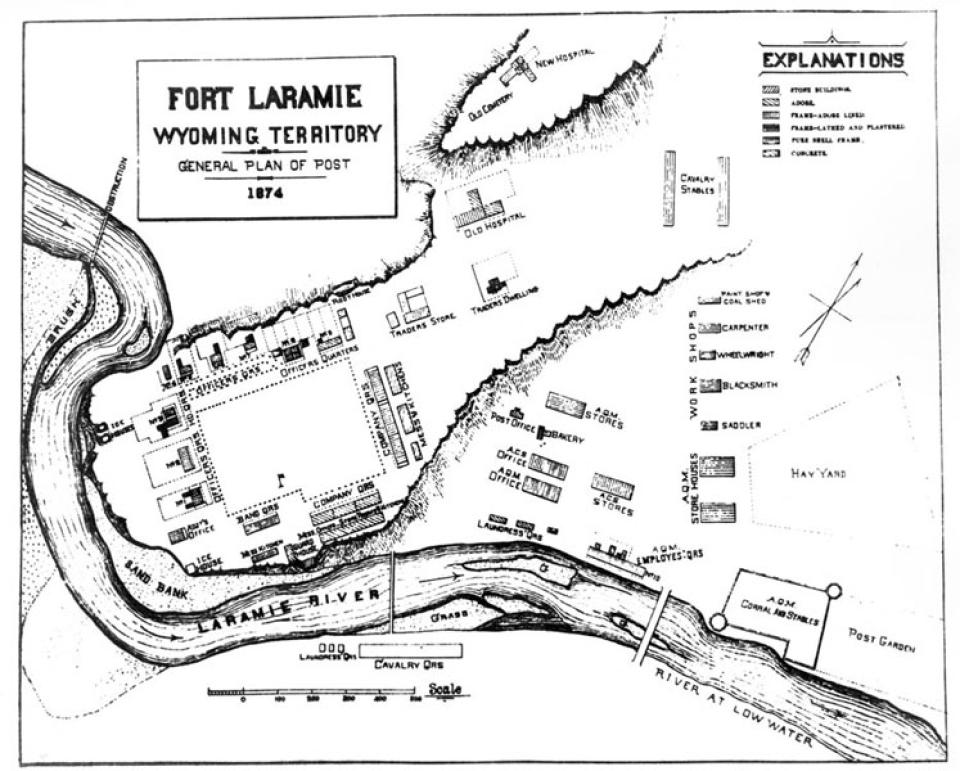
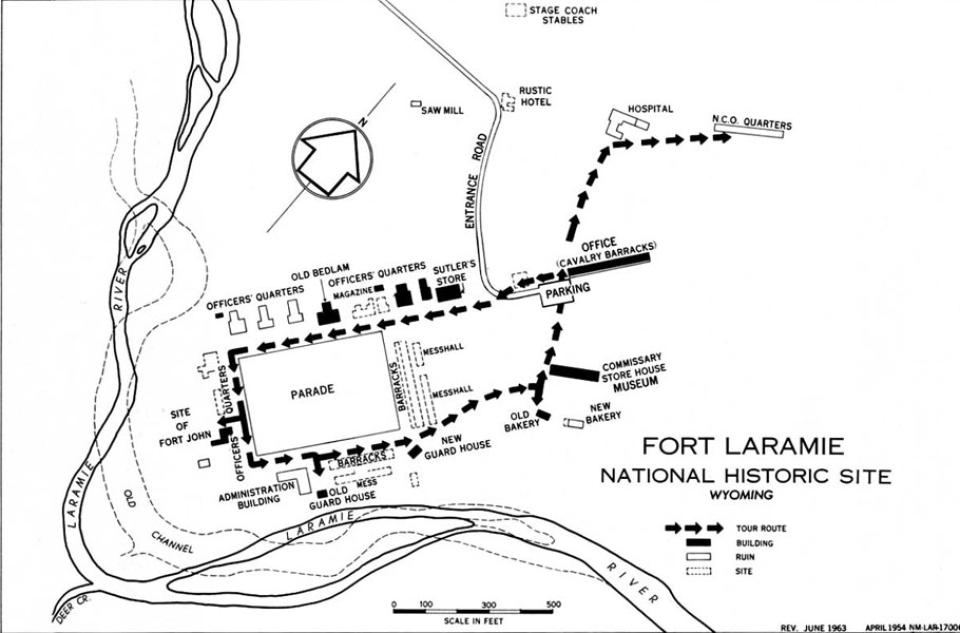
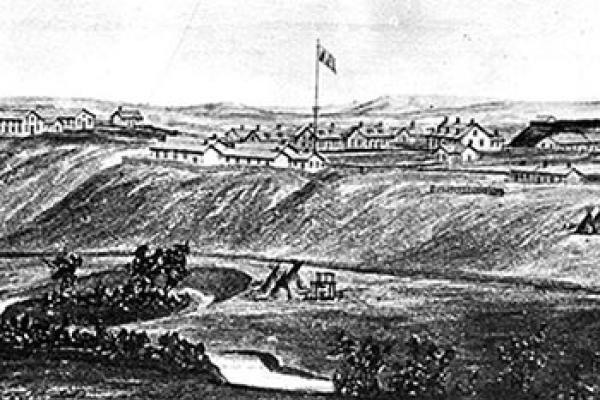
Fort Laramie began as a fur-trade post in 1834 near the confluence of the Laramie and North Platte rivers. Soon it changed into a post for the trade in buffalo robes, and for supplying emigrants bound west on the Oregon/California/Mormon Trail. In 1849 the post was purchased by the U.S. Army, and became an important supply, logistics and communications center for the Indian Wars campaigns of the next four decades. In recent decades the post has been carefully restored, and today is a National Historic Site.
Fort Fetterman was established by the U.S. Army on the North Platte River near present Douglas, Wyo. in 1867. It served as a staging point for Gen. George Crook’s three campaigns against Cheyenne and Lakota Sioux Indians in 1876, near the end of the Indian Wars. The Army abandoned the post in 1882, and the settlement finally closed down a few years later when the railroad arrived at Douglas, seven miles to the south.
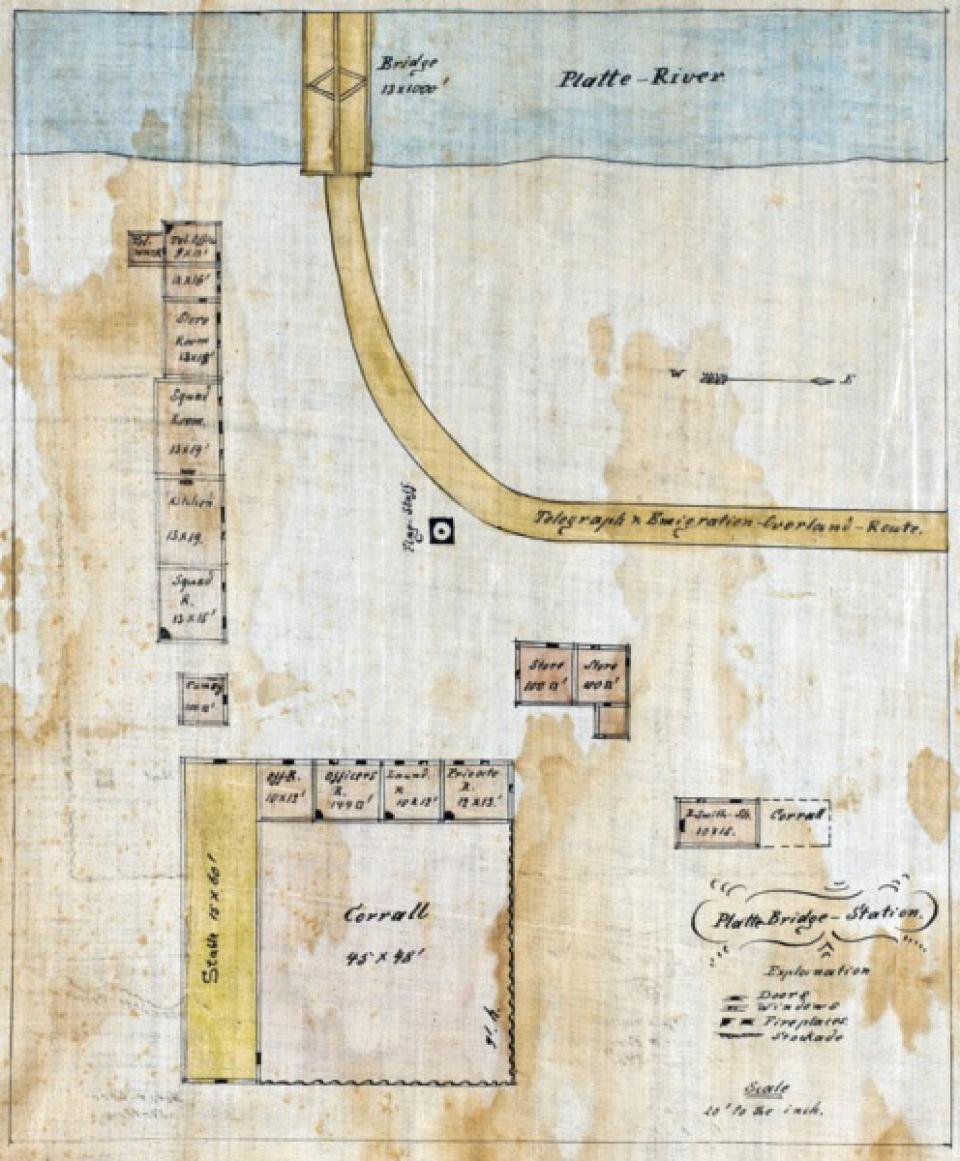
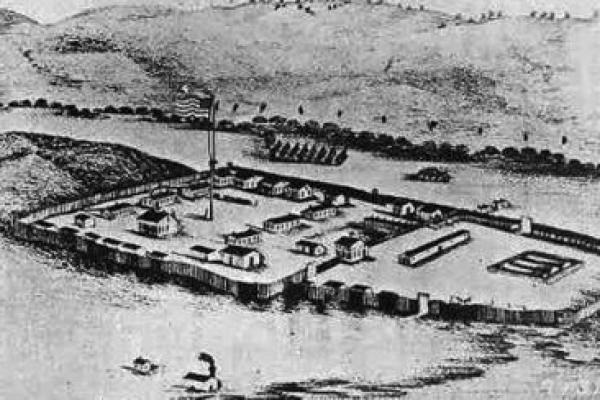
The U.S. Army established Platte Bridge Station in 1862 to protect the Oregon/California/Mormon Trail crossing of the North Platte River and the new transcontinental telegraph. After Lt. Caspar Collins was killed there by Cheyenne and Lakota Indians in 1865, the post was renamed Fort Casper, misspelling his first name. The fort was abandoned two years later, but reconstructed in 1936—and renamed Fort Caspar—with funds from the Works Progress Administration. Fort grounds and a museum are open to the public.
Two military posts were built a few miles apart during the Indian Wars near the strategic Bozeman Trail crossing of Powder River—Fort Reno in the 1860s and Cantonment Reno in the 1870s. The first was one of three forts whose existence provoked the tribes into war. The second was an important Army base for later campaigns.
Fort Phil Kearny, near present-day Story, Wyo., was established by the U.S. Army in the summer of 1866 to protect travelers on the Bozeman Trail from Indian attack. and abandoned two years later, under terms of the1868 Treaty of Fort Laramie. Indians burned the fort shortly after the army left.
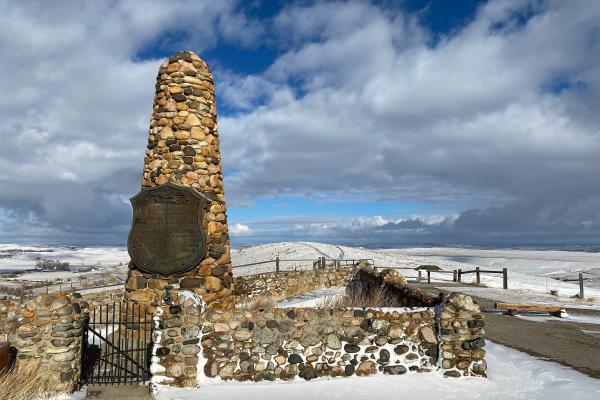
The Fetterman Battlefield, southeast of present Story, Wyo., marks the spot where Capt. William Fetterman and all 80 men under his command were killed Dec. 21, 1866 by Lakota Sioux, Cheyenne and Arapaho Indians.
On Aug. 2, 1867, a large force of Oglala Sioux attacked woodcutters near Fort Phil Kearny. Soldiers assigned to protect the woodcutters took cover behind a ring of wagon boxes. After the intense battle, both sides claimed victory, and estimates of the dead and wounded varied widely.
The Connor Battlefield is a park on Tongue River in Ranchester, Wyo., marking the spot where Brig. Gen. Patrick Connor and about 475 U.S. troops and Pawnee scouts in August 1865 attacked a village of 500 Arapaho under the leadership of Black Bear and Old David. The Arapaho suffered 33 killed, and the troops burned their lodges and drove off most of the horse herd. Today the park offers picnic grounds, a campground and a monument to the event.
Quizzes & Activities
Lesson Plans